Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
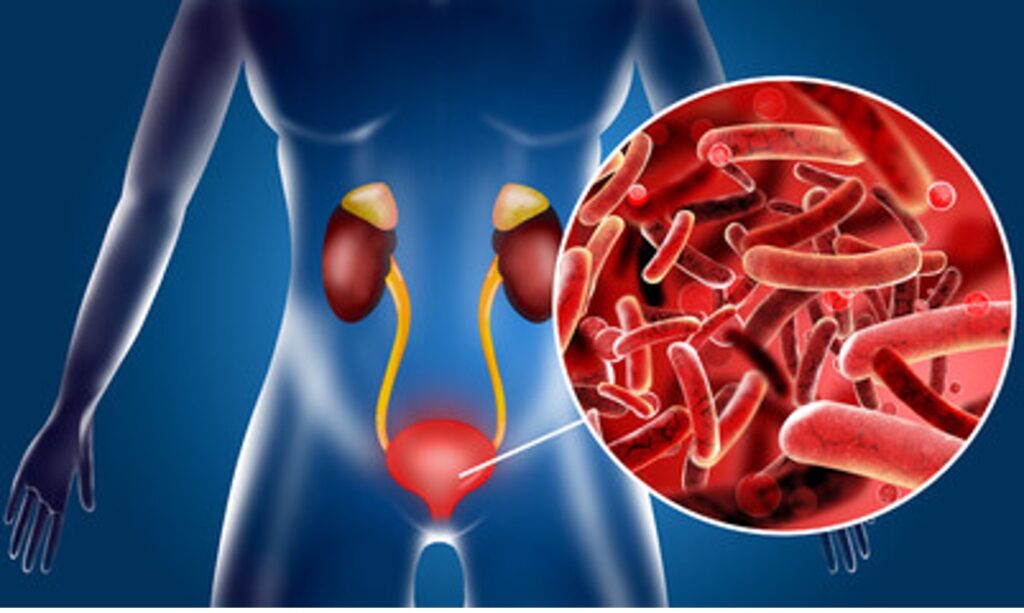
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that affect the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. They occur when harmful bacteria enter the urinary system, leading to discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. Although anyone can develop a UTI, women are more vulnerable due to their shorter urethras, which allow bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
Causes and Risk Factors

Several factors contribute to the development of UTIs. Holding urine for long periods, dehydration, and poor hygiene increase the risk of infection. Pregnancy, menopause, sexual activity, and a weakened immune system also make individuals more susceptible. Additionally, people with diabetes or urinary tract obstructions have a higher chance of experiencing recurrent infections. Understanding these risk factors can help in preventing UTIs.
Common Symptoms of UTIs
The severity of UTI symptoms varies from person to person. Common signs include:
✔ A frequent and urgent need to urinate
✔ A burning sensation while urinating
✔ Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
✔ Pelvic discomfort or lower abdominal pain
In severe cases, UTIs can lead to fever, chills, nausea, and back pain, indicating a possible kidney infection. Immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent complications.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Making simple lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of UTIs. Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract. Maintaining good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back after using the restroom, minimizes bacterial spread. Urinating before and after sexual activity also reduces the chance of infection. Additionally, avoiding harsh scented soaps and incorporating vitamin C-rich foods into the diet can support urinary health.
Effective Treatment and Recovery
UTIs are commonly treated with antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. Completing the full course of medication is essential to prevent antibiotic resistance and recurrent infections. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help ease discomfort during recovery. Additionally, natural remedies like cranberry supplements and probiotics may support urinary tract health. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is crucial to avoid complications.
By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals can lower their risk of urinary tract infections and maintain overall urinary health.