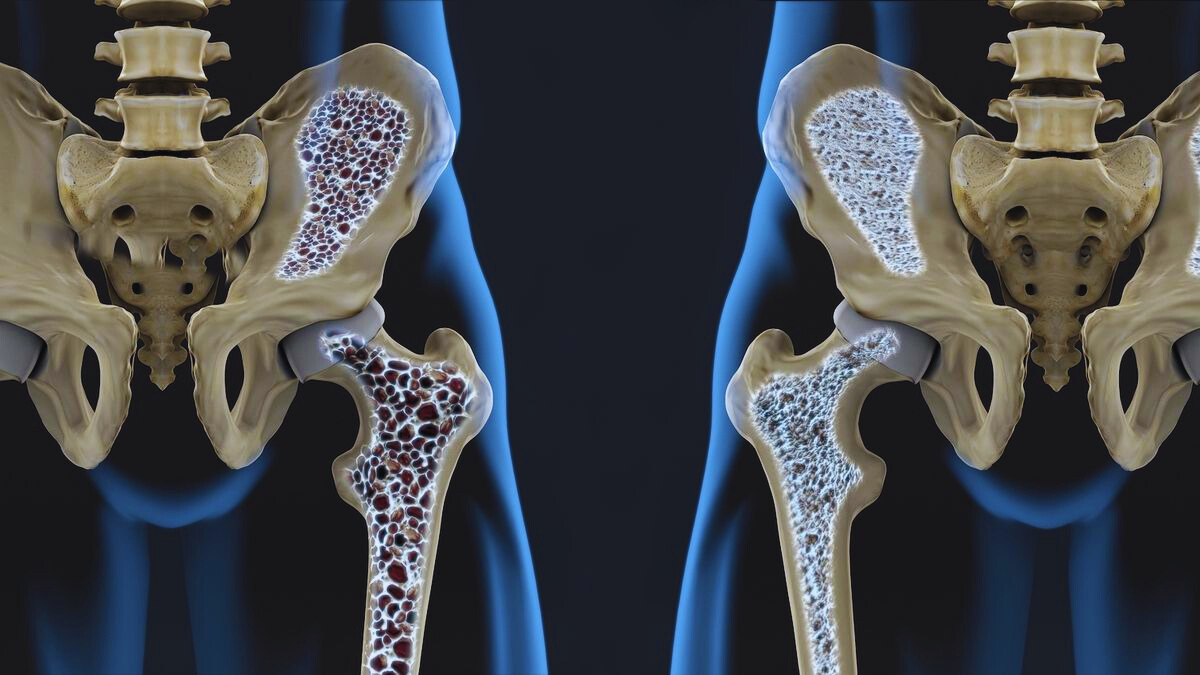
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. It develops when bone density decreases, leading to a higher risk of fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist. Osteoporosis often progresses silently, showing no symptoms until a fracture occurs. This is why early detection and preventive measures are crucial for maintaining bone health.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Aging is a major cause, as bone mass naturally declines with age. Women are at a higher risk due to hormonal changes after menopause, which lead to bone loss. Other risk factors include:
✔ Lack of calcium and vitamin D – Essential nutrients for strong bones
✔ Sedentary lifestyle – Lack of physical activity weakens bones over time
✔ Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption – Contributes to bone loss
✔ Genetics – Family history increases susceptibility
✔ Medical conditions and medications – Long-term use of steroids or conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can contribute to osteoporosis
Common Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it shows no symptoms in the early stages. However, as the condition worsens, individuals may experience:
✔ Frequent fractures – Especially in the hips, spine, and wrists
✔ Loss of height – A sign of spinal bone weakening
✔ Back pain – Due to fractured or collapsed vertebrae
✔ Poor posture – A stooped or hunched appearance due to weak spinal bones
Since symptoms are often unnoticed until a fracture occurs, regular bone density tests are recommended for early diagnosis.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing osteoporosis involves adopting a healthy lifestyle that supports bone strength. Some effective ways to maintain strong bones include:
✔ Balanced Diet – Eat foods rich in calcium (dairy, leafy greens) and vitamin D (sunlight, fish, fortified foods).
✔ Regular Exercise – Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and strength training help improve bone density.
✔ Healthy Habits – Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to protect bone health.
✔ Bone Density Tests – Regular screenings help detect early bone loss and prevent severe fractures.
Treatment and Management of Osteoporosis
While osteoporosis cannot be completely cured, various treatments can slow its progression and reduce the risk of fractures. Doctors may recommend:
✔ Medications – Prescription drugs like bisphosphonates help maintain bone density.
✔ Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements – Essential for strengthening bones.
✔ Physical Therapy – Improves balance and strength, reducing fall risk.
✔ Lifestyle Adjustments – Using assistive devices, improving home safety, and engaging in safe exercises can help prevent fractures.
By adopting a proactive approach through early detection, lifestyle changes, and medical intervention, individuals can effectively manage osteoporosis and maintain better bone health.






