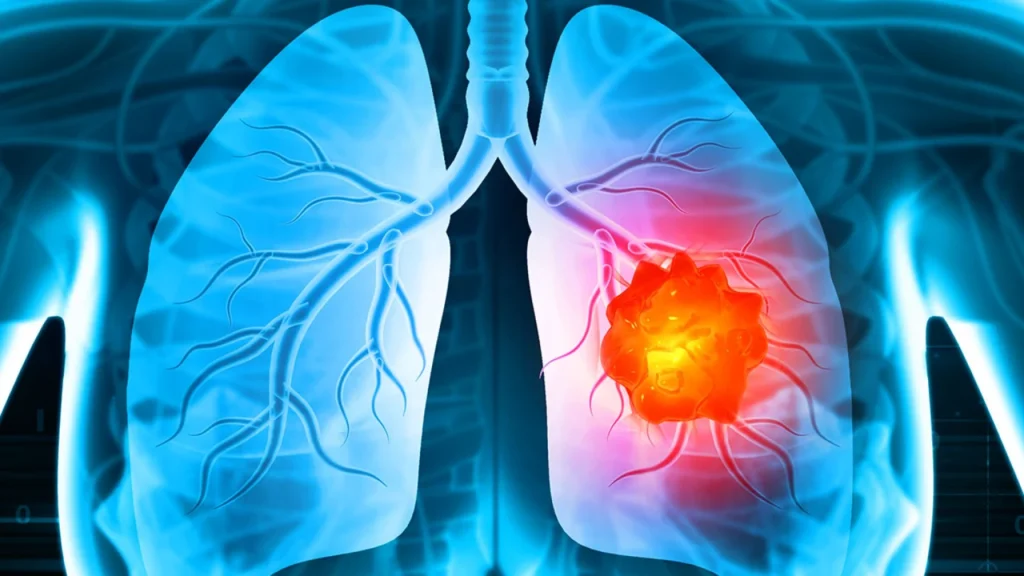
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a serious disease in which abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably in the lungs. It remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. However, early detection and timely treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to lung cancer development, including:
- Smoking: This is the primary cause, responsible for nearly 85% of cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Breathing in other people’s smoke can also increase the risk.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to toxins and pollutants can damage lung tissue.
- Radon Gas: This naturally occurring gas can accumulate in homes and increase lung cancer risk.
- Genetics: A family history of lung cancer may make some individuals more vulnerable.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Detecting lung cancer in its early stages can be difficult because symptoms often do not appear immediately. However, some common warning signs include:
- A persistent cough that worsens over time.
- Shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Unexplained fatigue and sudden weight loss.
- Coughing up mucus or blood.
- Frequent lung infections like bronchitis or pneumonia.
If any of these symptoms persist, seeking medical attention early can improve the chances of successful treatment.
Effective Treatment Options
Lung cancer treatment depends on the type and stage of the disease. Common treatment methods include:
- Surgery: Doctors remove tumors if the cancer is detected early.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medication travels through the bloodstream to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Specialized drugs attack specific genes or proteins linked to cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: The immune system is boosted to fight cancer cells more effectively.
Doctors often combine multiple treatments to improve survival rates and enhance quality of life.
Preventing Lung Cancer
Although not all cases are preventable, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
- Quit Smoking: This is the most effective way to lower lung cancer risk.
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Stay away from areas where smoking is common.
- Test for Radon: Regular home inspections can prevent exposure to harmful gases.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating nutrient-rich foods supports lung health.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity strengthens both the lungs and the immune system.
By adopting these habits, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing lung cancer and improve their overall well-being.