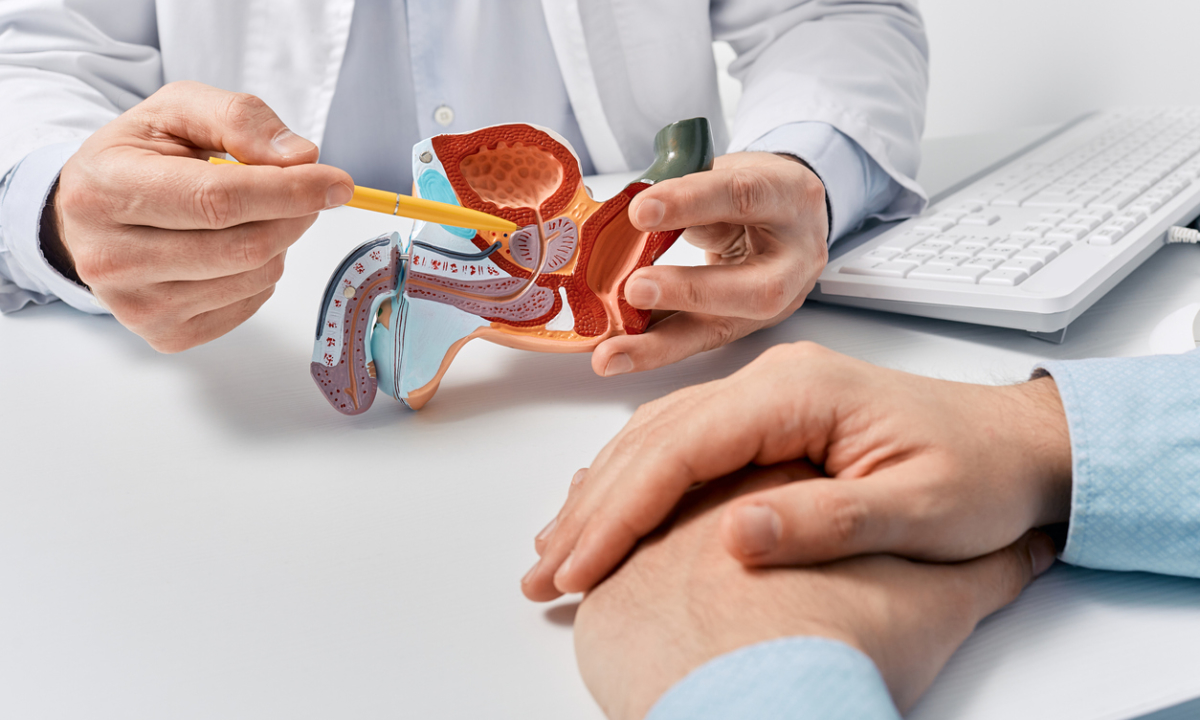
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer develops in the prostate, a small gland in men responsible for producing seminal fluid. It is one of the most common cancers among men, particularly those over 50. Some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and remain localized, while others spread aggressively to other parts of the body. Early detection and timely treatment significantly improve survival rates.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of prostate cancer. The most common risk factors include:
- Age: The risk increases significantly after 50.
- Family History: Men with close relatives who had prostate cancer are at a higher risk.
- Diet and Nutrition: Consuming excessive red meat, processed foods, and unhealthy fats may increase the risk.
- Hormonal Changes: Elevated testosterone levels can stimulate cancer cell growth.
- Obesity and Lifestyle: A sedentary lifestyle and excessive weight gain contribute to higher chances of developing prostate cancer.
Symptoms and Early Detection
In the early stages, prostate cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as it progresses, men may experience:
- Difficulty urinating or weak urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Chronic pain in the lower back, pelvis, or hips
- Frequent need to urinate, especially at night
- Unexplained weight loss and persistent fatigue
Regular prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal exams (DRE) help detect prostate cancer early, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Treatment Options
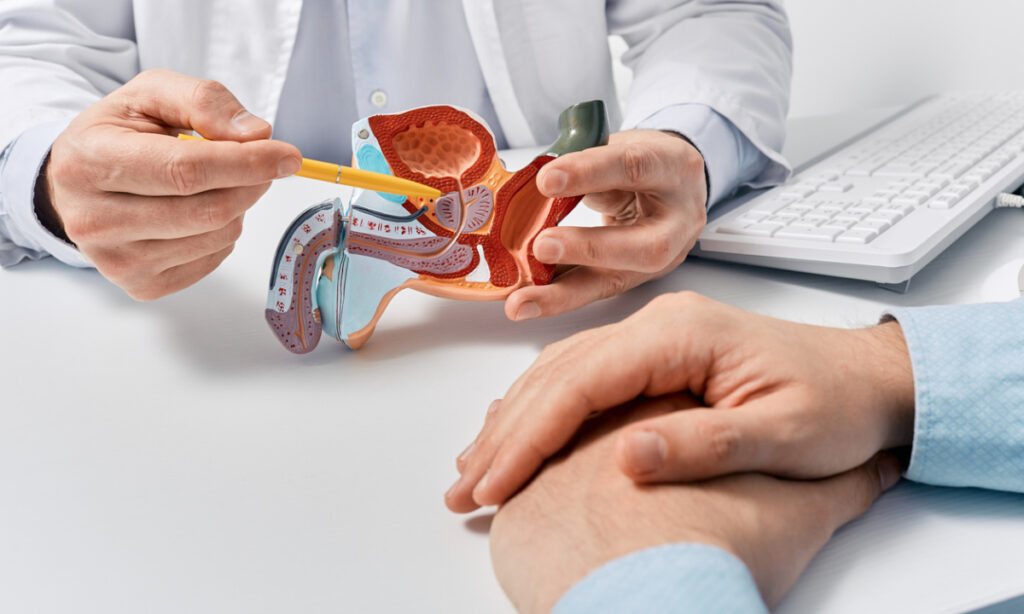
The treatment approach depends on the stage and severity of prostate cancer. Common treatment methods include:
- Active Surveillance: Doctors monitor slow-growing cancer without immediate treatment.
- Surgery (Prostatectomy): Removing the prostate gland eliminates cancerous cells.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells.
- Hormone Therapy: Lowering testosterone levels helps slow cancer growth.
- Chemotherapy: Used in advanced cases to attack cancer cells throughout the body.
- Immunotherapy: Strengthens the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Prevention Tips for a Healthy Prostate
Although prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
- Follow a Balanced Diet: Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps regulate hormones and maintain a healthy weight.
- Limit Processed Foods and Red Meat: Choose lean proteins and plant-based foods.
- Quit Smoking and Reduce Alcohol Intake: These habits contribute to overall health and lower cancer risks.
- Get Regular Check-Ups: Routine screenings, especially after 50, help detect cancer early.




